Oligonucleotide Therapeutics
Oligonucleotide therapeutics are chemical synthesized drugs the main skeleton of which is a chemically modified nucleotide.
Representative examples include antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), RNAi, aptamers and decoys.
Whereas oligonucleotide therapeutics act directly on mRNA, conventional gene therapies deliver a specific DNA gene sequence into the body to express mRNA and produce a protein having a particular function.
Oligonucleotide therapeutics have high specificity and can target specific molecules in cells, which is difficult with existing drugs such as mRNA or non-coding RNA molecules.
Moreover, it is easy to generate candidate agents within a short period because it is a product created by chemical synthesis.
Thus, the development of oligonucleotide therapeutics is advancing and will come into practical use as a next generation pharmaceutical.

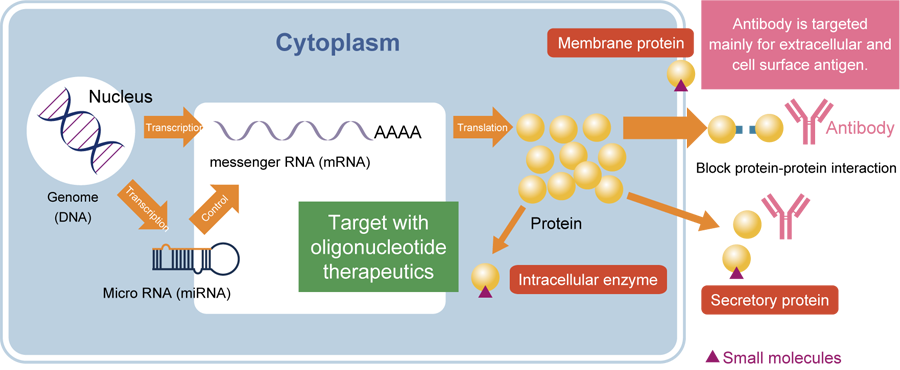
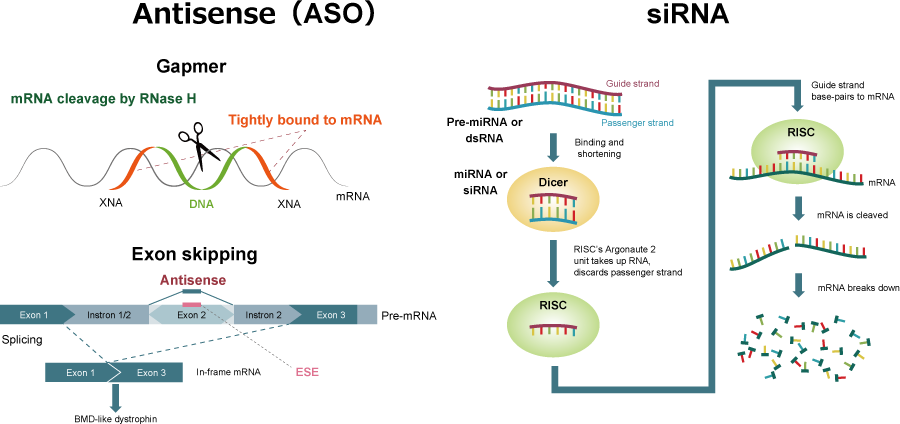
・By suppressing the cause of diseases upstream, a smaller amount will be effective.
・Oligonucleotide therapeutics can treat diseases dependent on “alignment” such as diseases caused by genetic mutations. Only oligonucleotide therapeutics can achieve this.